Orthopedic
Orthopedic surgery is a branch of medicine that deals with diseases related to bones and the musculoskeletal system. Some of these diseases include:
✔ Knee surgery
✔ Foot and ankle surgery
✔ Hip surgery
✔ Shoulder surgery
✔ Hand and wrist surgery
✔Prosthesis Applications
✔ Oncological Orthopedics
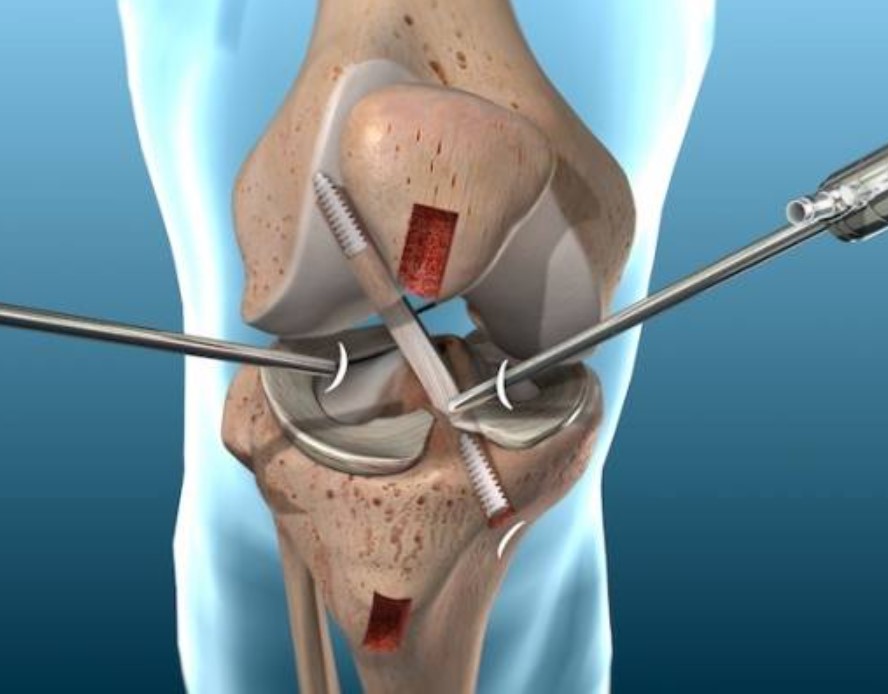
Knee Surgery
The knee is the joint we have the most problems with. The reasons for this can be explained as the fact that it is exposed to more loads than other joints, the two longest bones of our body make joints and its strength is provided only by soft tissues.
Interests in Knee Surgery:
✔ Sports injuries around the knee
✔ Knee peripheral fractures
✔ Knee ligament surgeries
✔ Knee cartilage surgeries and transplants
✔ Meniscus surgery
✔ Knee resurfacing prostheses, partial prosthesis, and total prosthesis
✔ Corrective surgeries for malalignment
Foot and Ankle Surgery
There are 30 joints in our feet, and we feel a load equivalent to 2-3 times our body weight when we move and 7 times our body weight when we run. It is inevitable for this joint structure to deteriorate over time.
Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Surgery Concerns:
✔ Deformities in the foot and ankle
✔ Problems with the big toe and other toes
✔ Bumps on the bone
✔ Bursae on the bone
✔ Bone cysts
✔ Sports-related injuries
✔ Trauma-induced fractures (heel, foot, ankle)
✔ Surgical procedures performed using Ilizarov technique (bone lengthening, fusion, shape correction)
Hip Surgery
The hip joint and pelvis, where this joint is located, allow us to perform movements such as standing, walking, and running. Conditions like improper development of the hip joint since birth, subsequent traumas, infections, osteoporosis, and tumors lead to complaints such as thigh pain, swelling, limping, and limited joint movements. Symptoms such as bad posture, limping, leg length discrepancy, hip pain, and discomfort around the thigh require referral to hip surgery.
Orthopedic Hip Surgery Concerns:
✔ Hip Dislocations (Adult and Child)
✔ Hip Joint Cartilage Problems
✔ Bone and Joint Infections
✔ Tumors
✔ Sports Injuriesı
✔ Fractures and Dislocations
Shoulder Surgery
The shoulder, one of the most detailed areas in orthopedic surgery, can be a significant source of problems, especially for athletes and the elderly. The shoulder region consists of three main bones. Ligaments, muscles, and tendons connect these bones together and move them. Repeated strenuous activities, accidents, and sports performed with incorrect technique lead to the wear and tear of these tissues. Wear and tear manifest as pain and movement restriction in the early period and calcification in the later period.
Orthopedic Shoulder Surgery Concerns:
✔ Shoulder Dislocation
✔ Shoulder Peripheral Fractures
✔ Shoulder Joint Calcification
✔ Rotator Cuff Tears-Impression Syndrome
✔ Joint Dislocations
✔ Joint Degeneration
✔ Tendon Problems
✔ Frozen Shoulder (frozen shoulder)
✔ Calcified Tendinitis
Spinal Surgery
Spinal surgery is a branch of medicine that deals with congenital or acquired curvatures of the spine, spinal degeneration due to aging, humps, fractures resulting from osteoporosis, spinal cord damage due to trauma, spinal inflammations, and spinal tumors.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition in which the spine curves to the right or left. In the early stages of scoliosis, there are usually no symptoms, but as scoliosis progresses, the following symptoms may occur:
✔ One shoulder may be higher than the other, with one shoulder blade sticking out more than the other.
✔ When the arms hang down at the sides, one side may have more space between the arm and the body.
✔ One hip may appear higher or more prominent than the other.
✔ When the patient is viewed from behind and asked to bend forward, one side of the back may appear higher than the other, creating a hump-like appearance on the back.
While the exact causes of scoliosis are not fully known, there is some evidence that scoliosis may be linked to genetic factors. Scoliosis is a condition that can affect the health and future of children during their growth stage.
When scoliosis is diagnosed early, the success rate of treatment is very high. However, if undetected curvatures of the spine are severe, they can hinder the normal growth of children. In adulthood, problems such as lower back and back pain, heart and lung function disorders can occur.
The treatment of scoliosis varies depending on the type and degree of scoliosis, but the most common treatments include:
✔ Observation: In patients with temperatures below 20 degrees whose skeletal growth is nearing completion, monitoring and regular check-ups may be sufficient. Monitoring continues until the patient’s skeletal development is complete.
✔ Brace treatment: The purpose of bracing is to try to prevent the progression of curvature. Bracing can be particularly effective in children whose curvature exceeds 25 degrees and who are still growing.
✔ Surgical treatment: Surgical treatment is required in children whose curvature exceeds 50 degrees and who are still growing. Curvatures exceeding 50 degrees continue to increase even after growth is complete.
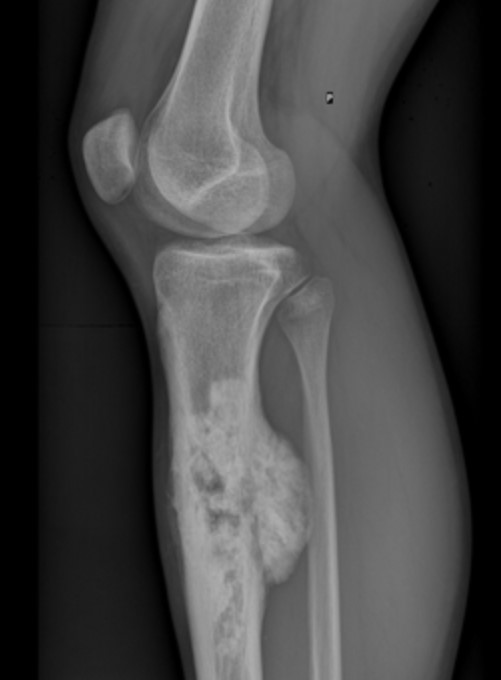
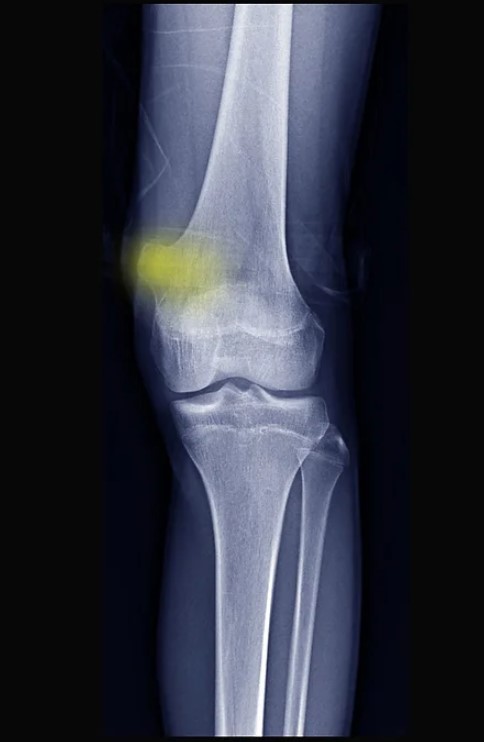
Orthopedic Oncology
Orthopedic Oncology is the branch of diagnosis and surgical treatment of bone and soft tissue tumors that develop in the musculoskeletal system and tumor masses that have spread to the bone (metastasis) from other organs.
Bone Tumors
Orthopedic oncology is the branch that diagnoses and surgically treats bone tumors and soft tissues that occur in the musculoskeletal system and mass tumors that have spread (metastasized) to the bones from other organs.
Bone tumor is an abnormal growth in bone tissue that invades and replaces healthy tissues, weakening the bones and causing fractures. The cause of most bone tumors is unknown.
If left untreated, they can lead to the loss of function of the affected organ or even death. Most bone tumors are benign and do not threaten life.
Malignant bone tumors include:
Osteosarcomas: Malignant tumors that spread to the bones from other organs.
Multiple Myeloma: The most common primary bone cancer.
Ewing’s Sarcoma: Typically develops in individuals aged 5 to 20 years, causing bone destruction with a large mass of soft tissue.
Chondrosarcomas: A type of bone tumor that usually appears as a mass in the hip, pelvis, or shoulder between the ages of 40-70.
Most patients with tumors suffer from continuous pain. Pathological fractures may occur, increasing the severity of pain. Some tumors cause symptoms such as fever and night sweats. Sometimes, they may appear as painless masses.
The treatment of benign bone tumors varies depending on the type of tumor and the age of the patient, but in most cases, monitoring is sufficient.
In some cases, medication reduces pain. Some may disappear on their own over time (especially in children). In some types of tumors, their recurrence may occur even if the mass is removed. Some benign tumors can also turn into malignant tumors over time.
The most important factor in treating malignant bone cancers is the type and stage of the tumor. Treatment may include surgical removal of the tumor alone or removal of healthy tissue surrounding the tumor. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy may also be used in combination with other treatments.
Soft Tissue Tumors
Soft tissues are the tissues located outside the structural system that surround and support various anatomical structures. Soft tissues account for about half of the body’s weight. They typically do not cause symptoms. However, symptoms such as loss of appetite, fever, and weight loss may occur. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy can be used in treatment, but surgical excision is the ultimate solution.
Diagnostic Methods Used in Orthopedic Surgery
The basic diagnostic methods used in orthopedics are:
✔X-ray
✔Ultrasonography
✔CT (Computed Tomography)
✔MR Imaging
✔Bone scintigraphy
✔Angiography
✔Biopsy
X-Ray
X-rays are a fast and painless method for imaging the body’s structures, especially bones. X-rays pass through your body. However, they appear absorbed depending on the density of the material they pass through. Dense materials like bones and metals appear white in X-rays. Air in the lungs appears black. Fat and muscles appear in shades of gray.
Ultrasonography
This method uses ultrasound waves to image the internal structure of the body. Ultrasound waves have a much higher frequency than what the human ear can hear. When ultrasound waves hit different tissues, they reflect in different ways. These reflections create images of tissues and organs on the ultrasound machine’s screen. This way, abnormal tissues like cysts and tumors can be detected.
Doppler ultrasonography is used to determine blood flow in vessels and associated diseases. In this method, sound waves are sent, but with the movement of blood, there are changes in sound frequencies. Thanks to these changes, information about the speed and direction of blood flow can be obtained.
CT (Computed Tomography)
This method allows X-rays to image tissues and organs in the body in a cross-sectional view. CT scans provide more detailed information than regular X-rays. They are especially used in diagnosing head injuries, brain tumors, and other brain diseases. CT scans can also visualize bones and soft tissues, as well as blood vessels through computed tomography angiography.
MR Imaging
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that does not involve harmful radiation like X-rays. In MRI, images are created using radiofrequency waves in a strong magnetic field. MRI, which is highly effective in imaging soft tissues, can detect cancerous areas that cannot be found using other methods.
Bone Scintigraphy
It is a method to examine the entire body at once. It is used to determine whether the tumor has spread to the bones. In the initial stage of the examination, the radioactive material is injected into the vein. Then, at regular intervals, any part of the bones that accumulates more radioactive material is examined more. Inflammation in the bone may be associated with a tumor or may be due to other causes such as trauma or infection.
Angiography
It is used for imaging the arteries in certain parts of the body, and it is the best method that can be used to show the vascular properties of the tumor. It is usually needed when planning before surgery.
Biopsy
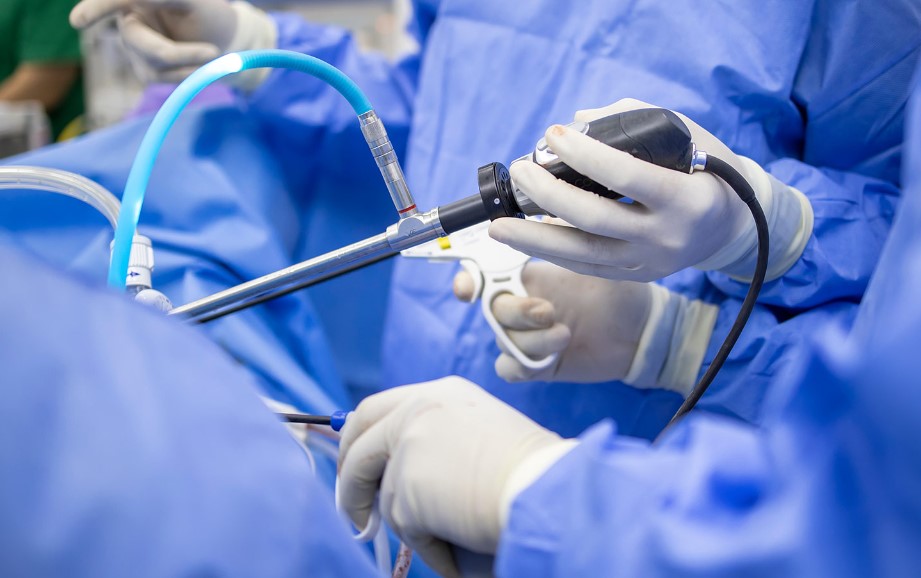
A biopsy is the process of taking a small piece of body tissue and examining it under a microscope. The tissues taken are usually subjected to some microbiological and molecular biology tests. Biopsies are typically performed in suspected disease cases. For example, if there is a tumor or an abnormal mass in the body, a biopsy must be done to determine whether it is a tumor or not. Arthroscopy is performed by inserting devices of medium thickness (about 4 mm) from the skin into the joint after inflating it with water by injecting water into the joint. It is a more useful method compared to open surgery in terms of the risk of infection, pain after surgery, and cosmetic appearance.
Treatment Methods Used in Orthopedics
The main treatment methods used in orthopedics are as follows: ✔Arthroscopy ✔ Prosthetic applications ✔ Bone lengthening surgeries
Arthroscopy
Following the inflation of the joint with water, it is made in the form of insertion of an average of 4 mm devices in the joints through the skin. It is an advantageous method compared to open surgery in terms of reducing the risk of infection, the amount of postoperative pain, and poor cosmetic appearance.
Prosthetic Applications
It is a method for replacing joints with artificial parts. The destruction and deformity of cartilage in the joints occur for various reasons.
These conditions cause pain, restrict movement, and cause disability. Therefore, the joint surfaces need to be renewed and treated. Completely replacing the joint is a surgical procedure. Metal and plastic materials used for joint prostheses come in different shapes according to the type, shape, movement, and size of the joint. The orthopedic surgeon decides which one is suitable using special measurement systems and special X-rays. Metal and plastic materials in joint prostheses are attached to the bone using acrylic (bone cement). Some artificial joints are attached to the bone by special structures (screws, etc.) on the bone-facing surfaces. The patient’s recovery time after surgery varies depending on the patient and the joint. Custom prostheses for elderly patients can be used for life, and no second surgery is required. If it is necessary to perform this surgery on young patients, second renewal procedures and sometimes third ones can be performed.
Bone Lengthening Surgeries
Bone lengthening surgeries, especially provide a solution for shortening of the arms and legs due to paralysis, fractures, inflammations, and some bone diseases. Limb lengthening can be performed for cosmetic purposes in a type of dwarfism called achondroplasia. In these patients, it is possible to lengthen the legs by up to 20-25 cm and the arms by up to 10-12 cm, provided that it is started early. Nearly 90% of satisfactory results are achieved in patients who are selected correctly and closely monitored.