Test-tube babies
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is one of the assisted reproductive techniques used to help couples who cannot conceive naturally. In this treatment, a woman's eggs are taken from her ovaries and combined with the man's sperm in a laboratory to achieve fertilization. The fertilized eggs (embryos) are then placed into the woman's uterus, awaiting pregnancy.
People who can undergo the process of in vitro fertilization (IVF):
✔ If a woman’s fallopian tubes are blocked.
✔ If a man has a lower-than-normal sperm count, reduced sperm motility, or abnormal sperm morphology.
✔ For couples who have not been able to achieve pregnancy using other artificial insemination methods.
✔ For couples with unexplained infertility.
✔ For women suffering from intra-abdominal tissue diseases due to adhesions, which cannot be treated by other means, making pregnancy impossible.
✔ For those with specific hormonal disorders.
✔ For couples who have not been able to achieve pregnancy using other therapeutic means.
✔ For couples who wish to identify specific genetic diseases in embryos and aim to have a healthy child using preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD).
✔ For women who have experienced recurrent miscarriages and wish to choose healthy embryos.

Stages of artificial insemination treatment:

✔ Preparation Stage: Patients interested in IVF start by taking birth control pills at the beginning of their menstrual cycle. These pills are used to regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent the formation of ovarian cysts before starting treatment.
In the following menstrual cycle, the ovaries are stimulated using hormonal medications. These medications promote the growth of multiple eggs and increase the chances of pregnancy.
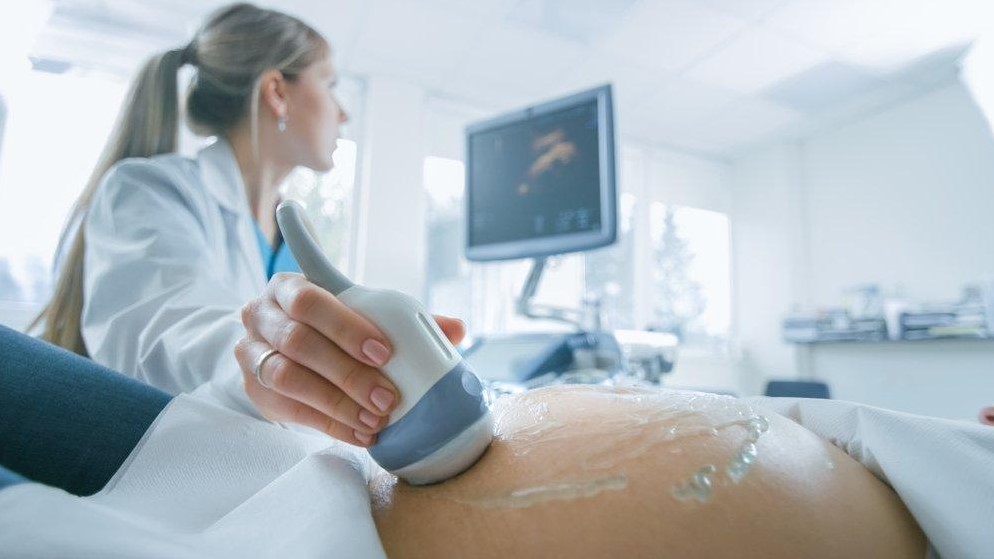
✔ Ovarian Development and Monitoring: The growth of mature eggs is monitored using ultrasound. When the eggs reach a certain size, an injection is administered to trigger ovulation.
✔ Egg Retrieval: Approximately 36 hours after the ovulation trigger injection, the woman’s eggs are collected.
✔ Sperm Sample Collection:A sample of sperm is collected from the man on the same day that the eggs are retrieved.
- Fertilization:
The woman’s eggs and the man’s sperm are fertilized in the laboratory, either using the standard IVF method or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) depending on sperm quality. In ICSI, sperm is directly injected into the egg to achieve fertilization.
✔ Embryo Formation: Embryos form after the fertilization process.
✔ Embryo Transfer:Selected and healthy embryos are transferred to the woman’s uterus between days 2 and 4 after fertilization.
✔ Waiting for Pregnancy:A 12-day waiting period follows embryo transfer to see if the embryos successfully implant in the uterus.
✔ Pregnancy Test: On the 12th day after embryo transfer, a pregnancy test is conducted to determine the outcome.
Methods used in artificial insemination treatment:
The standard method for artificial insemination treatment (IVF): Eggs and sperm are combined in the laboratory, allowing fertilization to occur naturally
Microscopic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
In the tube baby method, the sperm given by the man and the eggs taken from the woman are brought together in the laboratory, and fertilization is expected to occur automatically. Sperm with insufficient fertilization capacity, few movements, and severe deformity cannot pierce the egg spontaneously and fertilization cannot be achieved. In such cases, sperm is injected into the egg, and fertilization is achieved. This operation is called microinjection (ICSI).
TESE and TESA Methods
TESE (Testicular Sperm Extraction) and TESA (Testicular Sperm Aspiration) techniques are used for men who have problems with sperm production or release.
TESE involves taking a tissue sample from the testicle using a needle.
TESA involves surgically taking a tissue sample from the testicle.
Nondrug Tube Baby (IVM)
Artificial insemination without medication (IVM): Involves collecting immature eggs and maturing them in the laboratory instead of using medications.
This method is used for patients who are sensitive to the drugs used to stimulate egg growth.
