Urologye
Urology is a surgical medical specialty that deals with diseases related to the urinary tract and male reproductive organs. Urology addresses problems associated with the following organs:
✔Kidneys
✔Urine channels
✔Bladder
✔Prostate gland
✔Semen channels
✔Urethra
✔Testis
Urology deals with both adult and pediatric patients and has the following subspecialties:
✔Pediatric Urology
✔Andrology (Diagnosis and Treatment of Sexual Dysfunctions)
✔Urological Oncology (Uro-oncology)
✔Female Urology- Urogynecology
✔Neuro-urology
✔Kidney Diseases
Fields of Interest in Urology
Pediatric Urology
The main areas of interest in pediatric urology include:
✔Undescended testis
✔Hydrocele (Water hernia)
✔Hirospadias
✔Voiding disorders
Undescended Testis
An undescended testicle is a condition where the testicles do not descend into the scrotum after birth. This condition may spontaneously resolve within the first 10-12 months after birth. If it doesn’t resolve during this time frame, surgical intervention is necessary.
The surgical treatment involves bringing the testicles down into the scrotum and securing them there. If undescended testicles are left untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as infertility and testicular cancer. In addition, hernias are commonly seen in children with undescended testicles, and these hernias are often repaired during surgery.
Hydrocele (Water Hernia)
Hydrocele occurs when the canal between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum fails to close after birth. It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid around one or both testicles, which can be intermittent or constant.
Once diagnosed, hydrocele is generally expected to resolve and improve by the end of the first year of life. If it does not, a small surgical procedure can be performed to resolve the issue.
Hypospadias
Hypospadias is a condition where the urinary opening is not at the tip of the penis but opens somewhere lower. It is found in one out of every 300 male infants and comes in varying degrees of severity.
In severe cases, it can lead to serious problems such as preventing proper and forward urination, causing the penis to remain curved during erection, and preventing semen from reaching its desired location. The only treatment for hypospadias is a careful surgery performed by experienced hands. The most suitable time for surgery is between 1 and 2 years of age.
Urinary Disorders
Another condition commonly seen in children but often overlooked until serious problems arise is urinary disorders. These disorders can manifest in various ways, such as nighttime or daytime bedwetting, difficult and painful urination, holding in urine for extended periods, and frequent urination. They require a detailed and thorough urological examination.
If urinary disorders are not taken seriously and are ignored, they can sometimes lead to dangerous consequences like severe kidney infections, organ damage, and even kidney failure.

Andrology (Diagnosis and Treatment of Sexual Dysfunctions)
Andrology is a medical specialty that deals with male and female sexual health as well as male infertility. Its areas of interest include:
✔Erectile dysfunction in men
✔Female sexual dysfunctions
✔Male infertility
Erection Defects in Men
Erectile dysfunction is a common problem, affecting one in every ten men. It is defined as the inability to achieve or maintain the level of firmness required for sexual intercourse. It is more commonly seen in men over the age of 40. Men with erectile dysfunction typically have normal other sexual functions.
The causes of erectile dysfunction include:
 ✔Psychological reasons
✔Psychological reasons
✔Vascular diseases
✔Nervous system diseases
✔High blood pressure and diabetes
✔Smoking
✔Medications used
The choice of treatment depends on whether the cause is physical or psychological. If the issue is psychological, seeking support from a specialized psychologist in sexual therapy is recommended.
For erectile dysfunction related to physical causes, there are four main treatment methods:
✔ Oral medications
✔ Vacuum pump
✔ Penile injections: Vasodilators are injected into the penis with a thin needle. These medications work by relaxing the penile tissue and dilating blood vessels.
✔ Penile prosthesis: A penile prosthesis consists of two artificial cylinders implanted into the penis through surgery. The prosthesis does not affect urinary function or other sexual functions such as ejaculation and orgasm.
These treatment methods do not eliminate the root cause of the problem but rather enable achieving the level of erection necessary for sexual intercourse.
Female Sexual Dysfunctions
Sexual dysfunction in women can arise from various physical and psychological factors, with a prevalence rate of around 40%. Sexual dysfunction in women is classified as follows:

✔ Low Sexual Desire
A decrease or absence of sexual desire, or even aversion to sexual activity, can occur due to physical and psychological reasons.
✔ Arousal Disorders
Women with arousal disorders do not experience sufficient arousal during foreplay and sexual intercourse to experience pleasure. Causes may include systemic diseases (such as diabetes), hormonal issues, menopause, medication use, and nerve damage resulting from surgical interventions.
✔ Painful Sexual Intercourse (Dyspareunia)
In medical terms, it is referred to as “dyspareunia,” which is the experience of pain during sexual intercourse. Approximately 30% of women experience pain disorders after surgical interventions on the female genital organs, and among women who present with this complaint, 40% have medical problems related to their reproductive organs.
✔ Vaginismus
Vaginismus involves the involuntary contraction of the outer one-third of the vagina during sexual intercourse, preventing the entry of the penis. It can occur as a result of trauma, rape, surgical interventions, or due to inflammatory diseases affecting the sexual organs and glands, as well as vaginal changes during menopause. Vaginismus can also be influenced by psychological factors or the environment in which an individual was raised. Medical treatment, psychotherapy, and sexual therapy may be required.
In the treatment of sexual dysfunction, the underlying cause is identified, and treatment is aimed at addressing the cause. There is a wide range of treatment options, from medication or device-based therapies like vacuum pumps to psychotherapy. Ongoing research continues to explore new treatment methods.
Male Infertility
Infertility is defined as the inability to fulfill the reproductive function. Male infertility can result from various causes, including sperm production disorders, blockages in the sperm ducts, the formation of antibodies against sperm, testicular trauma, hormonal disorders, anatomical problems, varicocele, past illnesses, infections, and certain medications.
To diagnose infertility, the patient’s medical history and habits (such as smoking) are first examined. Then, a physical examination is conducted. Diagnosis is supported by tests such as semen analysis, urine analysis, and hormone analysis.
Treatment is generally based on the underlying cause of the problem. Infections and hormonal disorders are treated with medication. Varicocele is treated if it affects sperm production or causes testicular shrinkage.
Urological Oncology
Urological oncology is a subfield of urology that deals with cancers of the urological organs.
Early diagnosis of urological cancers allows for effective treatment. The main areas of interest include:
✔ Prostate Cancer
✔ Bladder Cancer
✔ Kidney Cancer
✔ Testicular Cancers
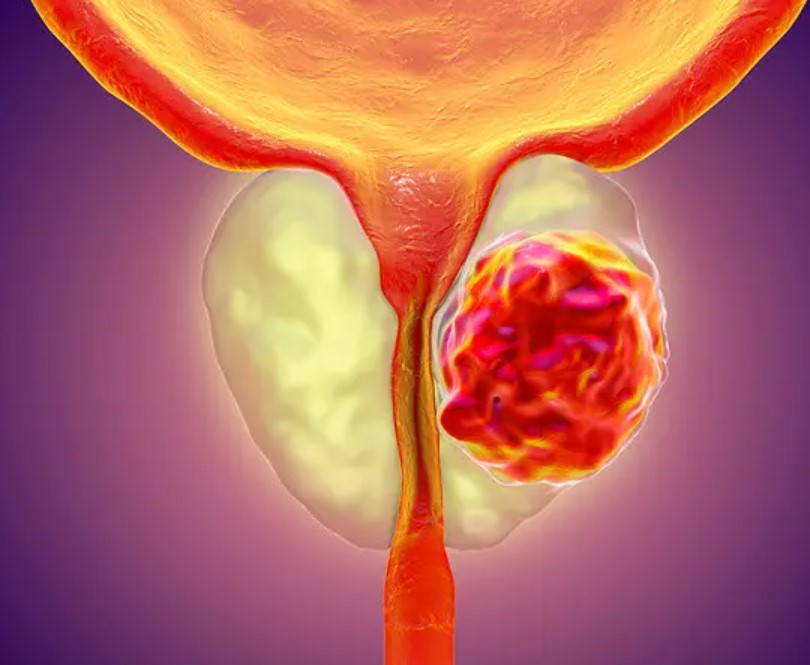
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a cancer that occurs only in men. Its exact cause is not fully understood, but age, race, and genetic factors are believed to play a role, with age being the most significant factor.
The incidence of prostate cancer significantly increases after the age of 50. Prostate cancer may not present symptoms in some individuals, but in others, it can lead to frequent, difficult, and painful urination, blood and inflammation in the urine, and urinary dribbling, among other symptoms.
Because prostate cancer progresses slowly, it can be treated with medication or surgical procedures.
Bladder Cancer
The bladder is responsible for storing and expelling urine. Bladder cancer occurs when the cells that make up the bladder multiply uncontrollably.
Early diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer often lead to a full recovery. This disease is more commonly observed in individuals who smoke and those working in industries involving dyes, chemicals, and rubber. The most common symptom of bladder cancer is blood in the urine. Treatment for superficial and less aggressive bladder cancer often involves transurethral resection (TUR) of the bladder tumor, followed by intravesical immunotherapy or chemotherapy to reduce the risk of recurrence.
In cases where the cancer has penetrated the muscle layer of the bladder, the standard treatment involves removing the bladder and constructing a new urinary reservoir from the intestine.
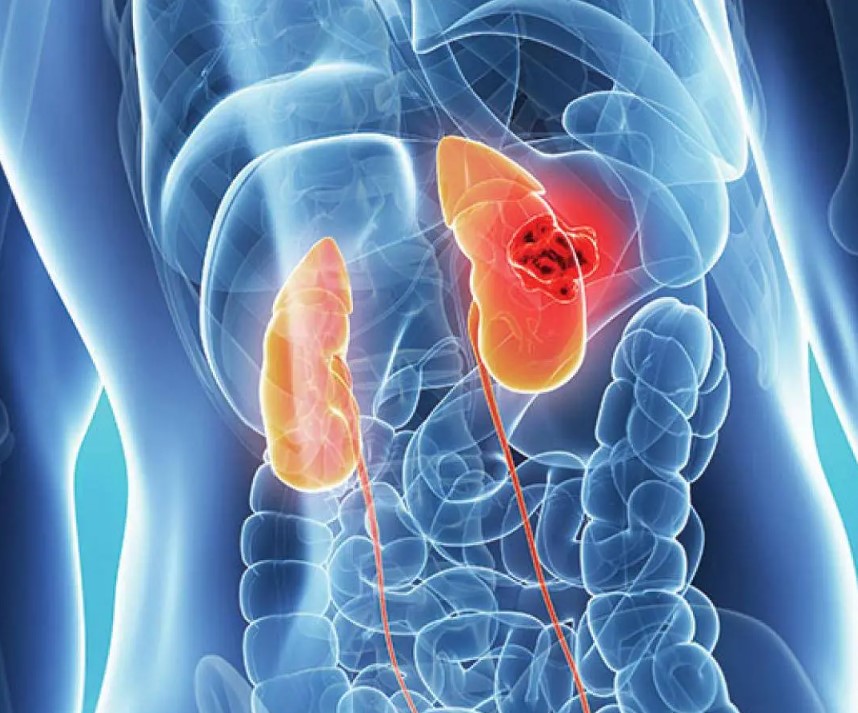
Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer is more common in individuals aged 50 to 70, with men being affected 2-3 times more often than women. While the exact cause of kidney cancer is not fully known, risk factors include smoking, genetic factors, high blood pressure, obesity, occupational risk factors (such as working in the steel, petroleum, cadmium, lead, and other industries), and exposure to radiation.
Kidney cancers may not show symptoms initially, but as the tumor grows, symptoms like blood in the urine, pain, loss of appetite, weight loss, frequent fevers, high blood pressure, and anemia can occur.
Surgery is the primary treatment for kidney tumors, and radiotherapy may be used as a supportive treatment alongside surgery.
Testicular Cancers
Testicular cancer is the most common cancer in young men and accounts for 1% of male cancers. It is more common in white men compared to other races.
Common symptoms of testicular cancer include pain, the presence of a mass or enlargement in one of the testicles. After surgical treatment for testicular cancer, chemotherapy may also be administered.
Female Urology (Urogynecology)
The main areas of interest in women’s urology, also known as urogynecology, include:
✔Involuntary urinary incontinence
✔Overactive bladder
✔Pelvic organ sagging
Involuntary Urinary Incontinence
The bladder serves two essential functions: storing and emptying urine. When the storage function of the bladder is disrupted, urinary incontinence can occur. This problem may not always originate solely from the bladder. Narrowing at the end of the urinary tract, urinary tract infections, and damage to the urinary retention mechanism can also lead to various types of urinary incontinence.
In women, especially during activities like laughing, coughing, and lifting heavy objects, urinary incontinence is a very common problem. Urinary incontinence is not a disease but a symptom. While it may not pose a life-threatening risk, it can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. After identifying the causes, treatment may begin with exercises or medication.
Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder is a condition that can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life. Individuals with an overactive bladder frequently need to use the restroom and may experience sudden urges to urinate, which can lead to urinary incontinence in more severe cases. According to research, up to 60% of women between the ages of 20 and 70 may experience this complaint at some point in their lives or continuously.

Pelvic Organ Prolapses
The displacement of pelvic organs such as the bladder, uterus, rectum, and intestines can lead to serious problems in both body structure and daily quality of life. Pelvic floor muscle exercises and biofeedback therapy can be used to treat this condition non-surgically in the early stages. In more advanced cases, simple surgical methods can help women overcome this problem.
Neuro-Urology
The functioning of all our organs, including urination, is controlled by the nervous system. Neuro-urology is a unit that manages the diagnosis and treatment processes of patients with urinary disorders resulting from diseases of the nervous system components, such as the spinal cord, brain, and peripheral nerves.
Kidney Diseases
✔Nephritis
✔Albumin
✔Kidney stones
✔Uremia
✔Kidney cancer
✔Kidney failure
Nephritis
Nephritis, also known as kidney inflammation, is a significant disease that can lead to kidney failure. Nephritis is divided into two types: microbial and non-microbial, depending on the causes. In rapidly progressing cases, chronic kidney failure may develop, and the patient may become dependent on dialysis. The treatment method for each patient is determined based on the results of kidney biopsy.
Albumin
Albuminuria is a disease caused by the improper functioning of the capsules that filter urine in our kidneys. When the kidney capsules do not filter sufficiently, protein leakage occurs in the urine.
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are formed when substances in the urine crystallize due to inflammation of the urinary tract, which blocks the flow of urine. Kidney stones can cause severe pain and bleeding in the kidneys. Most stones up to 5 mm in size can be eliminated through medication and increased fluid intake.
As the size of the stone increases, the likelihood of passing it naturally decreases. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), which involves breaking the stone using shock waves generated from outside the body, is the most common method for treating kidney stones. After the stone is fragmented, it is expected to pass out of the body with urine.
When the stone is larger than 2 cm or cannot be broken with ESWL, a current endoscopic surgical method called percutaneous nephrolithotripsy (PNL) is applied. In PNL, a small incision is made in the lower back under general anesthesia, and an endoscope is inserted into the kidney through this route. The stones are then removed whole or in fragments through the same route. Another surgical treatment method is ureteroscopy, in which a flexible ureteroscope is used to enter the ureter and break the stones with laser energy. The advantage of ureteroscopy is its flexibility, allowing access to even the most curved parts of the kidney.
Uremia
Uremia refers to harmful substances called urea that reach the kidneys through the bloodstream and need to be excreted through urine. When urea accumulates in the body instead of being excreted through urine, it leads to a condition called uremia. This disease occurs when the kidneys fail to filter urea adequately. Symptoms of this condition include constant headaches, blurred vision, hiccups, daytime drowsiness, and nighttime insomnia. Uremia is a disease that requires immediate treatment.
Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer is generally observed in individuals aged 50-70. It is 2-3 times more common in men than in women. Although the exact cause of kidney cancer is not fully understood, it is known that factors such as age, race, and genetics increase the risk. Among these factors, age is considered the most significant factor.
The incidence of prostate cancer significantly increases after the age of 50. Kidney cancers initially do not show many symptoms. However, as the tumor grows, symptoms such as blood in urine, pain, loss of appetite, weight loss, recurrent high fever, high blood pressure, and anemia can occur.
Surgery is the primary treatment method for kidney tumors. Radiation therapy can be used as a supportive treatment alongside surgery.
Kidney failure
The essential functions of the kidneys include maintaining the body’s water, salt, and calcium balance, eliminating harmful substances and drugs from the body through urine, and contributing to hormone and sugar metabolism. In kidney failure, there is a disruption in these kidney functions. Kidney failure can develop suddenly (acute) or slowly (chronic).
Causes of acute kidney failure include:
Severe bleeding, vomiting, diarrhea, a drop in blood pressure due to burns
Pregnancy-related complications, miscarriages in unhealthy conditions
✔ Heart failure
✔ Kidney diseases
✔ Urinary tract blockages
✔ Previous surgeries
Acute kidney failure due to medication is a common problem, so medications should always be used under a doctor’s supervision.
Causes of chronic kidney failure include:
✔ Nephritis
✔ Diabetes
✔ Hypertension
✔ Urinary tract diseases such as stones, obstructions, tumors
✔ Kidney cysts
Symptoms of kidney failure may include:
✔ Frequent urination at night
✔ Fatigue, shortness of breath, palpitations
✔ Decreased urine volume
✔ Hypertension
✔ Swelling in the hands, feet, and around the eyes.
Diagnostic Methods Used in Urology
The most commonly used diagnostic methods for urological diseases are as follows:
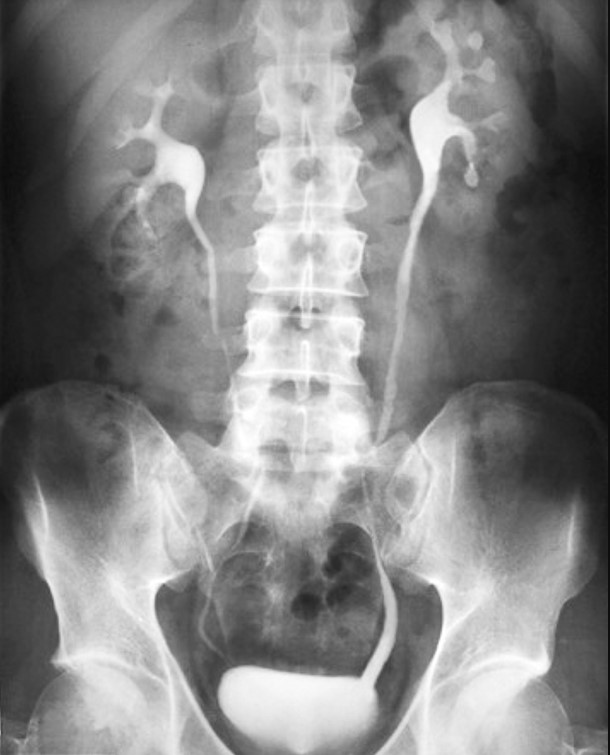
✔ IVP (Intravenous Pyelography)
✔ Ultrasonography
✔ Ultrasound-guided multi-prostate biopsy
✔ CT (Computerized Tomography) scan
✔ MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
✔ Scintigraphy
✔ Endoscopic examinations
✔ Urodynamic studies
✔ Sperm analysis (Spermiogram)
✔ VCUG (Voiding Cystourethrogram)
IVP
An opaque substance given intravenously is retained by the kidneys, and X-ray films are taken to visualize the kidneys and urinary tract.
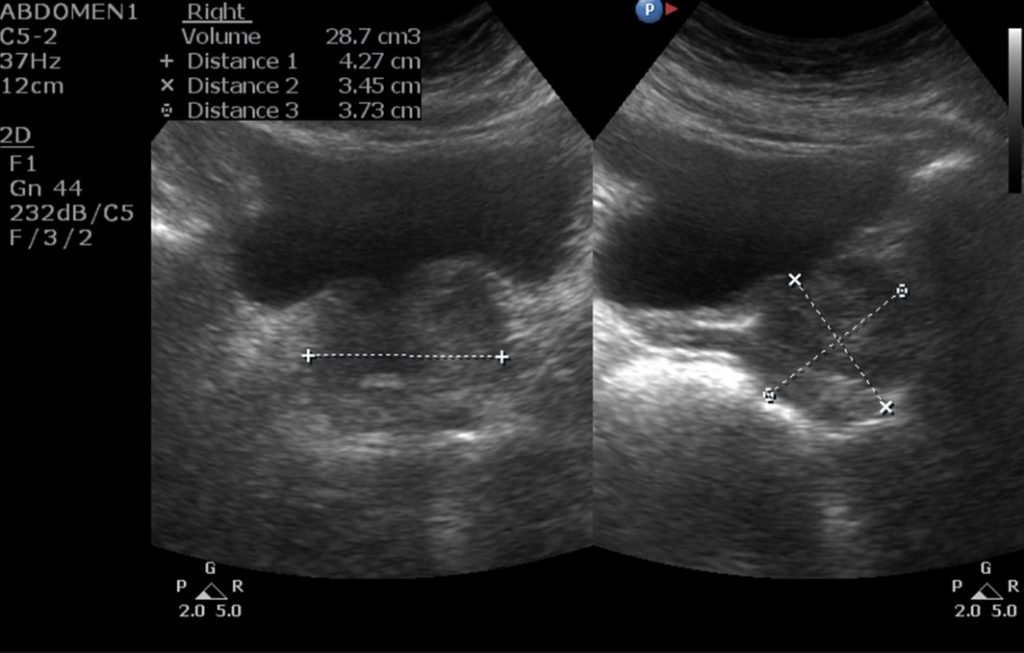
Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography uses sound waves to visualize the body’s internal organs. The sound waves used are at such a high frequency that they cannot be heard by the human ear. Since different tissues reflect sound differently, the resulting image varies. This allows for the visualization of tissues and organs on the ultrasound machine’s screen.
This method can provide different images of tissues such as cysts and tumors. Doppler ultrasonography, on the other hand, measures the amount of blood flow within a blood vessel and helps diagnose conditions that obstruct this flow. It also uses sound waves, but since blood is a moving structure, there are changes in sound frequencies that provide information about blood flow.
Ultrasound-Guided Multiple Prostate Biopsies
This procedure is necessary for diagnosing prostate cancer and is based on taking a sample from a suspicious area using ultrasound guidance.
CT (Computed Tomography)
CT scan is a special imaging method that uses X-rays to provide cross-sectional images of tissues and organs in the body. Compared to conventional X-ray images, CT scans can provide more detailed information about head injuries, brain tumors, and other brain diseases. CT scans can also visualize bones, soft tissues, and blood vessels.
MR Imaging
MRI, or Magnetic Resonance Imaging, is a diagnostic method that does not use harmful radiation such as X-rays and is painless. It is particularly successful in imaging soft tissues. In MRI, a strong magnetic field and radiofrequency waves are used to create images. Because soft tissues reflect these waves differently, MRI can detect cancerous areas that may not be visible with other diagnostic methods.
Scintigraphy
Scintigraphy is a technique that involves administering radioisotope substances through the bloodstream to visualize their retention and excretion in the kidneys. It is a highly useful method for tumor diagnosis.
Endoscopic Examinations
Cystoscopy: This is an examination performed by entering the urinary bladder through the external urethra under local or general anesthesia. Its advantage is that it allows direct observation of the bladder and the external urethra.
RGP (Retrograde Pyelography): During cystoscopy, a thin catheter is inserted into the kidneys, and then an opaque substance is injected to evaluate the kidney channels, renal pelvis, and internal urinary pathways. This examination is called retrograde pyelography and is used to assess kidneys and kidney pathways that are not adequately evaluated by other methods.
Ureteroscopy: It is a thinner and longer version of a cystoscope and is used to visualize the upper internal urinary pathway above the bladder.
Urodynamic Studies
This is a test used to measure bladder pressures and the urination process. The simplest form is uroflowmetry.
Spermiogram
A spermiogram is an examination that shows a person’s fertility. It is performed by analyzing semen collected from a male after ejaculation.
VSG
Vasography is an examination that shows the male reproductive system. Local anesthesia is used to locate the spermatic cord inside the scrotum, and an opaque substance is injected to visualize the sperm pathways.
Treatment Methods Used in Urology
✔Robotic surgery
✔ESWL (Stone breaking with sound waves from outside the body)
✔Kidney Transplant
Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery involves a surgeon’s console, robotic arms carrying instruments, and optical systems providing three-dimensional images. The surgeon controls it while sitting, which prevents fatigue during long surgeries and allows for better concentration.
Moreover, hand tremors are reduced by the robot, leading to improved surgical success. Robotic surgery results in faster recovery, particularly with less damage to sexual functions in prostate cancer cases. The advanced optical systems in this surgery provide a more detailed view compared to open surgery. Additionally, the operated area is magnified 12 times, causing less tissue damage, faster post-surgery recovery, and better oncological outcomes.
ESWL (Breaking the stone with sound waves from outside the body)
ESWL is an easy and comfortable treatment method. Stones are shattered using shockwaves and broken into small pieces, which are then expelled from the body through the urinary tract. Generally, this method successfully treats stones smaller than 2.5 cm in size, with an 85-90% success rate.
Kidney Transplant
Kidney transplantation is the procedure of placing a new kidney into the body through surgery when the existing kidneys cannot perform their functions adequately to sustain life and activities.
The dialysis process negatively impacts a patient’s life both mentally and physically. Before transplantation, a person leads a life dependent on dialysis, but after transplantation, they can regain their independence. Individuals who undergo kidney transplantation regain their strength, and improve their social and physical activities. Kidney transplantation can be performed from relatives or non-related individuals with compatible tissue. It is a highly successful procedure with a high success rate.